DeepDive
About Challenge.
Name : DeepDive.
Challenge Link : https://www.cyberdefenders.org/labs/78
Scenario : You are given a memory image of a compromised machine. Analyze the image and figure out the attack details.
Questions : 10
File Name : banking-malware.vmem
Tool : volatility
Solution
In this writeup we are using volatility 2.
1- What profile should you use for this memory sample?
To get the profile of the image we need to use imageinfo plugin.
vol.py -f banking-malware.vmem imageinfo
Output:
INFO : volatility.debug : Determining profile based on KDBG search...
Suggested Profile(s) : Win7SP1x64, Win7SP0x64, Win2008R2SP0x64, Win2008R2SP1x64_24000, Win2008R2SP1x64_23418, Win2008R2SP1x64, Win7SP1x64_24000, Win7SP1x64_23418
AS Layer1 : WindowsAMD64PagedMemory (Kernel AS)
AS Layer2 : FileAddressSpace (/home/******************/CyberDefenders/DeepDive/banking-malware.vmem)
PAE type : No PAE
DTB : 0x187000L
KDBG : 0xf80002bef120L
Number of Processors : 1
Image Type (Service Pack) : 1
KPCR for CPU 0 : 0xfffff80002bf1000L
KUSER_SHARED_DATA : 0xfffff78000000000L
Image date and time : 2021-02-09 00:51:25 UTC+0000
Image local date and time : 2021-02-08 22:51:25 -0200
2- What is the KDBG virtual address of the memory sample?
The answer of this question is in the output of the first one.
3- There is a malicious process running, but it is hidden. What is its name?
Since the process is hidden, we cannot find it using the pslist plugin as it’s a common procedure to unlink the process from ActiveProcessLink doubly-linked list in order to hide it.
It’s better to use psxview because it searches for any running process using 7 different methods (unlike other plugins which use only one method).
vol.py -f banking-malware.vmem --profile Win7SP1x64_24000 psxview
Output:
Offset(P) Name PID pslist psscan thrdproc pspcid csrss session deskthrd ExitTime
------------------ -------------------- ------ ------ ------ -------- ------ ----- ------- -------- --------
0x000000007e651b00 services.exe 500 True True True True True True False
0x000000007d9b4b00 svchost.exe 1772 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d2e5060 VSSVC.exe 2104 True True True True True True True
0x000000007da4bb00 lsm.exe 516 True True True True True True False
0x000000007d38cb00 vm3dservice.ex 2416 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d97f940 svchost.exe 356 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d827710 svchost.exe 636 True True True True True True True
0x000000007fe47b00 CompatTelRunne 996 True True True True True True True
0x000000007cf2fb00 WmiPrvSE.exe 3488 True True True True True True True
0x000000007da0a060 winlogon.exe 480 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d2735e0 dllhost.exe 2044 True True True True True True True
0x000000007fcf0b00 sppsvc.exe 3016 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d8ce920 WmiApSrv.exe 3692 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d68c6b0 OfficeClickToR 1232 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d353b00 dwm.exe 2236 True True True True True True True
0x000000007e770060 SDXHelper.exe 2828 True True True True True True True
0x000000007db38930 lsass.exe 508 True True True True True True False
0x000000007d2f3580 dllhost.exe 3188 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d5d7b00 WmiPrvSE.exe 1812 True True True True True True True
0x000000007e682b00 taskhost.exe 2344 True True True True True True True
0x000000007feb8b00 vmtoolsd.exe 1484 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d24d2f0 SDXHelper.exe 3200 True True True True True True True
0x000000007e5f45c0 svchost.exe 704 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d6bab00 VGAuthService. 1432 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d6dbb00 msdtc.exe 1968 True True True True True True True
0x000000007ddcf060 svchost.exe 916 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d336950 vds_ps.exe 2448 False False True True True True True
0x000000007d2508c0 conhost.exe 3028 True True True True True True True
0x000000007df7db00 SearchIndexer. 2616 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d678060 wmpnetwk.exe 856 True True True True True True True
0x000000007e8906d0 wininit.exe 412 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d33eb00 taskhost.exe 2192 True True True True True True True
0x000000007eae4060 CompatTelRunne 2984 True True True True True True True
0x000000007e1bfb00 svchost.exe 3324 True True True True True True False
0x000000007d69bb00 svchost.exe 1288 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d902060 svchost.exe 868 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d9ff610 svchost.exe 1132 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d3fc3e0 vmtoolsd.exe 2424 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d35db00 explorer.exe 2260 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d203930 dllhost.exe 1832 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d929370 audiodg.exe 1008 True True True True True True True
0x000000007db26b00 svchost.exe 3084 True True True True True True True
0x000000007e462b00 CompatTelRunne 2688 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d3535a0 taskeng.exe 2244 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d8a7b00 svchost.exe 756 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d24da30 SDXHelper.exe 3196 True True True True True True True
0x000000007d989b00 spoolsv.exe 1096 True True True True True True True
0x000000007ddc4060 svchost.exe 960 True True True True True True True
0x000000007fd4a6e0 ipconfig.exe 4008 True True False True False True False 2021-02-09 00:51:25 UTC+0000
0x000000007dde39a0 csrss.exe 360 True True True True False True True
0x000000007fc46b00 cmd.exe 3732 True True False True False True False 2021-02-09 00:51:25 UTC+0000
0x000000007ee7d6c0 smss.exe 272 True True True True False False False
0x000000007e9c6060 csrss.exe 424 True True True True False True True
0x000000007ffad860 System 4 True True True True False False False
0x000000007fc52060 conhost.exe 3848 True True False True False True False 2021-02-09 00:51:25 UTC+0000
The malware used 2 methods to hide, first by unlinking itself from the ActiveProcessLink list and then changing the process object signature.
4- What is the physical offset of the malicious process?
psxview plugin shows the physical address of each process, so you can use the 3rd question’s output to answer this question.
5- What is the full path (including executable name) of the hidden executable?
The easiest method to solve this question is to list all system files and gerp the malware name since we already got its name from the 3rd question.
vol.py -f banking-malware.vmem --profile Win7SP1x64_24000 filescan | grep <hidden_process_name>
6- Which malware is this?
This is such a funny question :D of course you can use the challege poster to solve this question.
But we will not do that.
We need to find the IOCs of this malware.
By IOCs we mean an obvious artifact of the malawre we can use to identify its family, but we will not go deep in the exe so we will just take a look at its strings.
Let’s start by extracting the process using its physical address from 4th question using procdump plugin.
vol.py -f banking-malware.vmem --profile Win7SP1x64_24000 procdump --offset=<process_physical_address> -D .
then use strings utility to search for any interesting string that might be unique in this malware.
Output:
snip
RegQueryValueExA
RegSetValueExA
ADVAPI32.dll
DragFinish
DragQueryFileA
SHELL32.dll
COMCTL32.dll
InterlockedExchange
UnregisterClassA
@P*w$@?97wKE9+Vey0babhTz2gVn_0Xb5q5sACHJ$qpLa@
l-rE
kernel32.dll
VirtualAllocExNuma
CreateDirectoryA
kernel32.dll
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET
LdrFin
dReso
urce_U
Acces
snip
@P*w$@?97wKE9+Vey0babhTz2gVn_0Xb5q5sACHJ$qpLa@ This string looks interesting, a quick google search linked it to a sandbox report which had the malware detected by a YARA rule.
7- The malicious process had two PEs injected into its memory. What’s the size in bytes of the Vad that contains the largest injected PE? Answer in hex, like: 0xABC
The process had two PEs injected into it, which means there are 2 protected VADs, either PAGE_EXECUTE_WRITECOPY or PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE and since there’s no dlls required by the executable so it may not have any FileObject.
Before developing a plugin to extract the VADs, I thought of using the malfind plugin to get the VADs addresses.
vol.py -f banking-malware.vmem --profile Win7SP1x64_24000 malfind --offset=<malware_physical_address>
Output:
Process: xxxx.exe Pid: xxxx Address: 0x220000
Vad Tag: VadS Protection: PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE
Flags: CommitCharge: 32, MemCommit: 1, PrivateMemory: 1, Protection: 6
0x0000000000220000 e8 00 00 00 00 58 89 c3 05 29 05 00 00 81 c3 29 .....X...).....)
0x0000000000220010 f7 01 00 68 01 00 00 00 68 05 00 00 00 53 68 80 ...h....h....Sh.
0x0000000000220020 7b 1c ed 50 e8 04 00 00 00 83 c4 14 c3 83 ec 48 {..P...........H
0x0000000000220030 83 64 24 18 00 b9 4c 77 26 07 53 55 56 57 33 f6 .d$...Lw&.SUVW3.
0x0000000000220000 e800000000 CALL 0x220005
0x0000000000220005 58 POP EAX
0x0000000000220006 89c3 MOV EBX, EAX
0x0000000000220008 0529050000 ADD EAX, 0x529
0x000000000022000d 81c329f70100 ADD EBX, 0x1f729
0x0000000000220013 6801000000 PUSH DWORD 0x1
0x0000000000220018 6805000000 PUSH DWORD 0x5
0x000000000022001d 53 PUSH EBX
0x000000000022001e 68807b1ced PUSH DWORD 0xed1c7b80
0x0000000000220023 50 PUSH EAX
0x0000000000220024 e804000000 CALL 0x22002d
0x0000000000220029 83c414 ADD ESP, 0x14
0x000000000022002c c3 RET
0x000000000022002d 83ec48 SUB ESP, 0x48
0x0000000000220030 8364241800 AND DWORD [ESP+0x18], 0x0
0x0000000000220035 b94c772607 MOV ECX, 0x726774c
0x000000000022003a 53 PUSH EBX
0x000000000022003b 55 PUSH EBP
0x000000000022003c 56 PUSH ESI
0x000000000022003d 57 PUSH EDI
0x000000000022003e 33f6 XOR ESI, ESI
Process: xxxx.exe Pid: xxxx Address: 0xxxxxxx
Vad Tag: VadS Protection: PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE
Flags: CommitCharge: 29, MemCommit: 1, PrivateMemory: 1, Protection: 6
0x000000000xxx0000 4d 5a 90 00 03 00 00 00 04 00 00 00 ff ff 00 00 MZ..............
0x000000000xxx0010 b8 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........@.......
0x000000000xxx0020 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
0x000000000xxx0030 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 b0 00 00 00 ................
0x000000000xxx0000 4d DEC EBP
0x000000000xxx0001 5a POP EDX
0x000000000xxx0002 90 NOP
0x000000000xxx0003 0003 ADD [EBX], AL
0x000000000xxx0005 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0007 000400 ADD [EAX+EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx000a 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx000c ff DB 0xff
0x000000000xxx000d ff00 INC DWORD [EAX]
0x000000000xxx000f 00b800000000 ADD [EAX+0x0], BH
0x000000000xxx0015 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0017 004000 ADD [EAX+0x0], AL
0x000000000xxx001a 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx001c 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx001e 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0020 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0022 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0024 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0026 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0028 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx002a 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx002c 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx002e 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0030 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0032 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0034 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0036 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0038 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx003a 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx003c b000 MOV AL, 0x0
0x000000000xxx003e 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
Process: xxxx.exe Pid: xxxx Address: 0xxxxx
Vad Tag: VadS Protection: PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE
Flags: CommitCharge: 55, MemCommit: 1, PrivateMemory: 1, Protection: 6
0x000000000xxx0000 4d 5a 90 00 03 00 00 00 04 00 00 00 ff ff 00 00 MZ..............
0x000000000xxx0010 b8 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........@.......
0x000000000xxx0020 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
0x000000000xxx0030 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 c8 00 00 00 ................
0x000000000xxx0000 4d DEC EBP
0x000000000xxx0001 5a POP EDX
0x000000000xxx0002 90 NOP
0x000000000xxx0003 0003 ADD [EBX], AL
0x000000000xxx0005 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0007 000400 ADD [EAX+EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx000a 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx000c ff DB 0xff
0x000000000xxx000d ff00 INC DWORD [EAX]
0x000000000xxx000f 00b800000000 ADD [EAX+0x0], BH
0x000000000xxx0015 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0017 004000 ADD [EAX+0x0], AL
0x000000000xxx001a 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx001c 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx001e 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0020 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0022 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0024 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0026 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0028 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx002a 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx002c 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx002e 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0030 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0032 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0034 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0036 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx0038 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx003a 0000 ADD [EAX], AL
0x000000000xxx003c c8000000 ENTER 0x0, 0x0
There are three injected VADs, one function and two executables.
The question asked about the largest VAD from the PE VADs so we will get all VAD info using vadinfo plugin then calculate the size between the start and end.
vol.py -f banking-malware.vmem --profile Win7SP1x64_24000 vadinfo -a <first_PE_VAD_address> --offset=<Malware_Physical_addresss>
vol.py -f banking-malware.vmem --profile Win7SP1x64_24000 vadinfo -a <second_PE_VAD_address> --offset=<Malware_Physical_addresss>
Output:
************************************************************************
Pid: xxxx
VAD node @ 0xzzzzzzzzzzz Start 0xxxxxxxxxx End 0xyyyyyyyyy Tag VadS
Flags: CommitCharge: 29, MemCommit: 1, PrivateMemory: 1, Protection: 6
Protection: PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE
Vad Type: VadNone
************************************************************************
Pid: xxxx
VAD node @ 0xzzzzzzzzzzz Start 0xxxxxxxxxx End 0xyyyyyyyyy Tag VadS
Flags: CommitCharge: 55, MemCommit: 1, PrivateMemory: 1, Protection: 6
Protection: PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE
Vad Type: VadNone
Calculate the size of each VAD (end - start) and the Answer is the largest number of them.
8- This process was unlinked from the ActiveProcessLinks list. Follow its forward link. Which process does it lead to? Answer with its name and extension
The malware process was unlinked from ActiveProcessLinks list by making the previous and forward processes point to each other instead of pointing to the malware, but the malware process points to the previous and forward processes.
Let’s start a volatlity shell session
vol.py -f banking-malware.vmem --profile Win7SP1x64_24000 volshell
change the current shell context to to the malware process:
cc(offset=<malware_physical_address> , phyiscal=True)
get the ActiveProcessLink value of the next process:
proc().ActiveProcessLinks.Flink
In many cases, I need to find the process using its ActiveProcessLinks value, so I developed a plugin to do that.
import volatility . plugins . common as common
import volatility . plugins . registry . registryapi as registryapi
import volatility . utils as utils
import volatility . win32 as win32
class GetProcByAcLin(common.AbstractWindowsCommand):
""" Get ActiveP list T """
def __init__( self , config , *args , **kwargs ):
common.AbstractWindowsCommand.__init__( self , config , *args , **kwargs )
self._config.add_option ( 'Search' , short_option = 't' , default = None , help = 'Ac Point Search For', action = 'store' )
def calculate(self):
addr_space = utils.load_as(self._config)
tasks = win32.tasks.pslist(addr_space)
T = self._config.Search
return T , tasks
def render_text( self , outfd , data ):
T , tas = data
try :
ishex = T.find("0x")
ishex2 = T.find("0X")
if(ishex>-1 or ishex2>-1 ):
T = int(T, 16)
else :
T = int(T)
for i in tas :
AcLin = i.ActiveProcessLinks
if T == AcLin :
print (i.ImageFileName)
except :
print("ActiveProcessLinks is a memory location : use number" )
Getting the process name:
vol.py --plugins="plug/" -f banking-malware.vmem --profile Win7SP1x64_24000 getprocbyaclin -t <Fprocess_ActiveLink_value>
9- What is the pooltag of the malicious process in ascii?
This question is very interesting.
It can be solved using many methods but the following method is the most interesting one, at least for me.
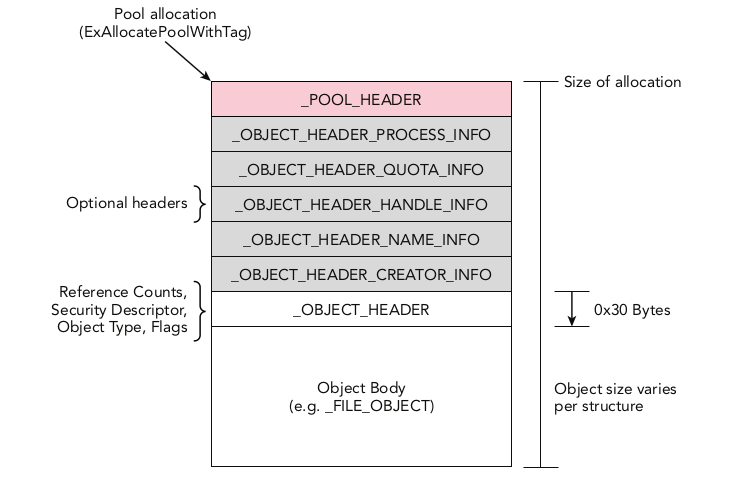
First you need to know about pool allocation for the page.
Page is structed of:
pool_headerwith size of 0x10 byte.Optional_headersize is deffrent from one to another.object_headerwith size 0x30 bytes.object_bodywith size of the object type itself.
But we need to find the pooltag for the process page which is part of pool_header struct.
We also need to jump to the pool_header object (Our method is by subtracting each header size from the physical address of the process).
But first, we need to know what optional header is used on this page, and we can find it from the object_header struct.
All we know is that our object body on this page is the Eprocess object and its physical address, so we need to go up by 0x30 byte in order to change the context to object_header struct.
We will start volshell from the malware eprocess object context:
cc(offset=<malware_physical_address> , phyiscal=True)
Then we will get object header context by going up 0x30 byte:
dt( "_OBJECT_HEADER" , <malware_physical_address>-0x30 , space=addrspace().base)
Output:
[_OBJECT_HEADER _OBJECT_HEADER] @ 0xxxxxxx
0x0 : PointerCount 149
0x8 : HandleCount 5
0x8 : NextToFree 5
0x10 : Lock xxxxxxxxxx
0x18 : TypeIndex 7
0x19 : TraceFlags 0
0x1a : InfoMask 8
0x1b : Flags 0
0x20 : ObjectCreateInfo 18446738026461179264
0x20 : QuotaBlockCharged 18446738026461179264
0x28 : SecurityDescriptor 18446735964826813854
0x30 : Body <malware_physical_address>
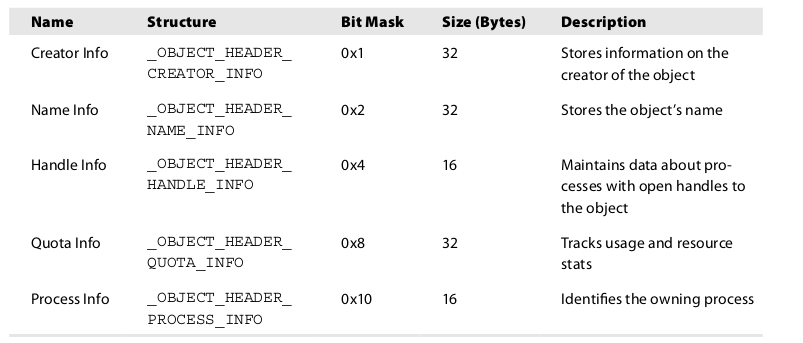
InfoMask value is referring to the used optional header.
InfoMask is 0x8 so the used optinal header is _OBJECT_HEADER_QUOTA_INFO and its size is 32 byte.
The pool_header start pointer is at malware_physical_address -0x30 -0x10 -0x20.
Now we are ready to get the pool_header object:
dt( "_POOL_HEADER" , <malware_physical_address>-0x30-0x10-0x20 , space=addrspace().base)
Output:
[_POOL_HEADER _POOL_HEADER] @ 0xxxxxxxx
0x0 : BlockSize 86
0x0 : PoolIndex 0
0x0 : PoolType 2
0x0 : PreviousSize 10
0x0 : Ulong1 39190538
0x4 : PoolTag int_four_bytes_reversed_pooltag
0x8 : AllocatorBackTraceIndex 0
0x8 : ProcessBilled 0
0xa : PoolTagHash 0
Convert the pooltag to 4 byte string in reverse order.
10- What is the physical address of the hidden executable’s pooltag?
You just need to add 4 bytes to the pool_header physical address.
POOL_HEADER_ADDRESS + 4